News & Events
Roadmap for a circular carbon plastics economy
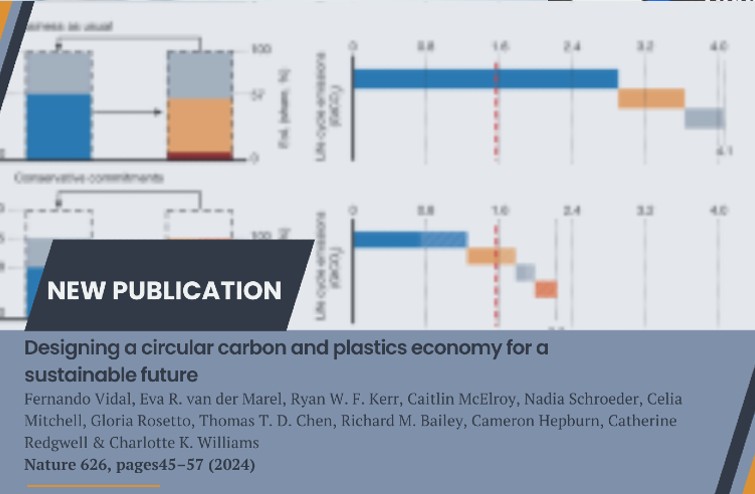
Researchers from the Oxford Martin Programme on the Future of Plastics, University of Oxford, have described ambitious targets to help deliver a sustainable plastic economy. The team includes Dr. Fernando Vidal, who signs as first-author, and is currently a senior postdoctoral researcher at POLYMAT. In a paper published in Nature, the authors analyse the necessary changes to our current technical, economic, and policy paradigms in order to mitigate carbon emissions and uncontrolled pollution from the plastic industry. The study includes a future scenario centred on four targets: cut demand by 50%; phase-out fossil-derived plastics in exchange for biomass alternatives; maximize recycling rates up to 95% of collected plastics; and do so while minimizing any negative environmental impacts. The authors go beyond in describing the future roadmap of interventions to help deliver these targets. Importantly, action must occur across all four target areas to ensure the global plastics systems curbs its climate impacts and meets UN Sustainable Development Goals.
In guiding this transition to a more sustainable plastics system, the authors set out principles to ensure ‘smart materials design’. Rather than one size fits all solution, these principles provide a careful consideration of the optimum production methods and appropriate use of resources, deliver the required performances, ensure waste management, and minimise broader environmental impacts.
Dr. Fernando Vidal is a Fulbright Scholar (2012), Newton International Fellow (2020), and Marie Skłodowska-Curie Individual Fellow (2021). He obtained his BSc in Chemistry (2011) from the University of Almería and MSc in Organometallics (2012) from the University of Alcalá de Henares. He graduated with a PhD in Chemistry from Colorado State University (2017) in the group of Prof. Eugene Y.-X. Chen. Since then, he has been a postdoctoral researcher in the groups of Prof. Frieder Jäkle at Rutgers University-Newark and Prof. Charlotte K. Williams at the University of Oxford. His current research interests align with bringing circular alternatives to polymer chemistry, specifically for applications in additive manufacturing.
The paper can be read here– https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06939-z







